Neural Scaling Laws: A Comprehensive Exploration
Definition and Background
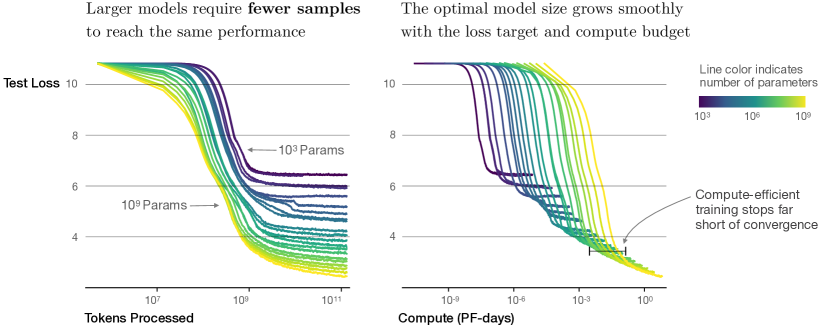
Neural scaling laws describe the empirical relationship between the performance of large-scale neural networks and their size, data availability, and computational resources. First identified in large language models and other AI systems, these laws provide insight into how scaling parameters like model size, dataset volume, and training duration influence the accuracy and generalization capabilities of AI systems.
The concept stems from the observation that many state-of-the-art models demonstrate predictable improvements in performance as they grow larger and are trained on more extensive datasets. These patterns are characterized by smooth power-law relationships, meaning performance scales predictably without abrupt changes or plateaus, given sufficient resources.
Phenomenon of Neural Scaling Laws
The key idea behind neural scaling laws is that larger models, when paired with proportionately larger datasets, exhibit improved performance. This phenomenon has been empirically validated across diverse AI tasks, including language modeling, image recognition, and reinforcement learning. Scaling laws suggest diminishing returns but maintain that these returns remain significant at large scales. For example:
- Model Size: Increasing the number of parameters in neural networks generally enhances their expressive capacity, enabling them to learn more complex functions.
- Dataset Size: Expanding the training data reduces overfitting and improves generalization, provided the data is diverse and high quality.
- Compute Resources: Prolonged training on larger models and datasets enables the system to achieve better optimization of parameters.
Challenges and Limitations
While neural scaling laws provide a roadmap for achieving better AI performance, they are accompanied by significant challenges:
- Resource Intensity: Training models at the scale suggested by these laws demands massive computational power and energy resources. For instance, training a model like GPT-4 requires thousands of GPUs operating over weeks or months.
- Data Scarcity: As dataset sizes grow, the availability of high-quality, diverse data becomes a bottleneck. Diminishing returns are observed when low-quality or redundant data is added.
- Environmental Impact: The carbon footprint of large-scale training is a pressing concern, with energy-intensive processes contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Diminishing Returns: Although scaling improves performance, the cost of these improvements grows disproportionately as models reach massive scales.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Researchers and organizations are actively exploring ways to address these challenges while leveraging the benefits of neural scaling laws:
- Algorithmic Innovations: Techniques such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning, sparsity, and pruning aim to achieve performance improvements with fewer resources.
- Synthetic Data: Generating synthetic datasets can help address data scarcity, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality training data.
- Energy-Efficient Hardware: The development of specialized AI hardware, such as TPUs and GPUs optimized for deep learning, reduces the energy consumption of training large models.
- Knowledge Distillation: This technique involves training smaller models to replicate the performance of larger ones, making deployment more feasible.
Notable Research and Contributions
Several pivotal studies and contributions have shaped our understanding of neural scaling laws:
- Kaplan et al. (2020): This seminal study quantified the scaling laws for language models, demonstrating the predictable improvement of large models trained on extensive datasets.
- Chinchilla Scaling Laws: Researchers at DeepMind proposed updated scaling laws emphasizing the balance between model size and dataset scale for optimal performance within fixed computational budgets.
- Scaling Vision Models: Studies extending scaling laws to computer vision tasks have revealed similar trends, affirming their generalizability across domains.
- Reinforcement Learning Applications: Neural scaling laws have also been applied in reinforcement learning, showing the importance of scaling environment interactions and model capacity.
Future Directions
The field of neural scaling laws continues to evolve, with several promising directions:
- Beyond Scaling: Exploring architectural innovations that break away from reliance on brute-force scaling.
- Fairness and Bias Mitigation: Ensuring that scaled models do not amplify biases present in the training data.
- Open-Access Models: Developing resource-efficient models that democratize AI access for smaller organizations and research groups.
Neural scaling laws provide a powerful framework for understanding and predicting AI performance improvements. By addressing associated challenges and optimizing scaling strategies, the AI community can continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with machine learning systems.
The Heart of AI Innovation in Korea
108, Taebong-ro, Seocho-gu, Seoul 06764, Republic of Korea
Tel. +82 2-958-0746
© National AI Research Lab 2024. All rights reserved.
If you have any problems with the website or need technical support, please contact inquiry@dvn.ci

